Taxonomic Categories

Taxonomic Categories
Classification is a hierarchical process of organizing living organisms into groups based on shared characteristics. Each level in this hierarchy is a taxonomic category, and all the categories together form the taxonomic hierarchy. Each category represents a rank or taxon.
Taxonomic Hierarchy
The major taxonomic categories, in descending order, are:
- Kingdom: The broadest category (e.g., Kingdom Plantae, Kingdom Animalia)
- Phylum/Division: For plants, the term “division” is used. All animals with a notochord and dorsal hollow neural system are in Phylum Chordata.
- Class: Related orders are grouped into a class. Order Primata (monkeys, gorillas, gibbons) and Order Carnivora (tigers, cats, dogs) are in Class Mammalia.
- Order: Assemblage of families with some similar characters. Plant families Convolvulaceae and Solanaceae are in Order Polymoniales. Felidae and Canidae are in Order Carnivora.
- Family: Group of related genera with fewer similarities than genus or species. Genera Solanum, Petunia, and Datura are in Family Solanaceae. Panthera (lions, tigers, leopards) and Felis (cats) are in Family Felidae.
- Genus: A group of related species with more characters in common than species of other genera. Solanum includes tuberosum (potato) and melongena (eggplant). Panthera includes leo (lion), pardus (leopard), and tigris (tiger).
- Species: The most basic unit, a group of individuals with fundamental similarities. Mangifera indica (mango), Solanum tuberosum (potato), and Panthera leo (lion) are examples of species.
Key Points
- Species: Defined by fundamental similarities and distinct morphological differences. The scientific name includes the genus and species (e.g., Homo sapiens).
- Genus: Genera are aggregates of closely related species.
- Higher Categories: As you move up the hierarchy (family, order, class, phylum/division, kingdom), the number of common characteristics decreases.
Examples
- Species: Mangifera indica, Solanum tuberosum, Panthera leo, Panthera tigris, Solanum nigrum, Solanum melongena, Homo sapiens
- Genus: Mangifera, Solanum, Panthera, Homo, Felis
- Family: Solanaceae, Felidae, Canidae
- Order: Polymoniales, Carnivora
- Class: Mammalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Kingdom: Plantae, Animalia
Table 1.1 From NCERT
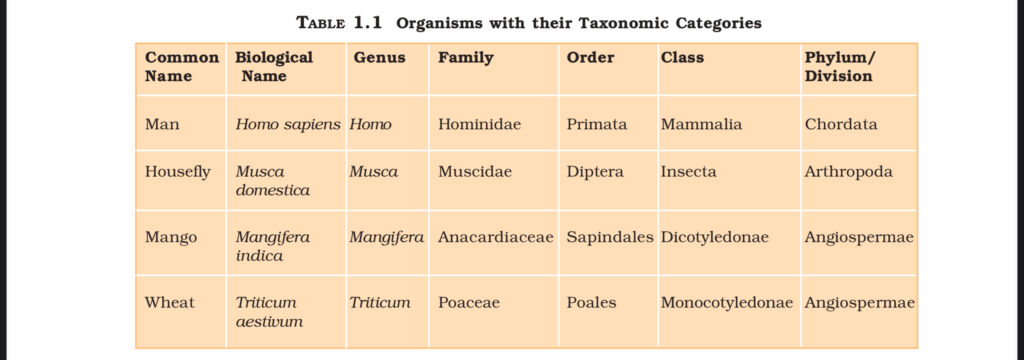
The table provides a clear illustration of the taxonomic hierarchy using examples of Man, Housefly, Mango, and Wheat. It shows how each organism is classified from species to kingdom.
Important Considerations
- Classification becomes more complex at higher levels of the hierarchy.
- Taxonomic categories represent distinct biological entities, not just morphological aggregates.
