Laws of Chemical Combinations

Laws of Chemical Combinations Notes
1. Law of Conservation of Mass
- In all physical and chemical changes, there is no net change in mass during the process.
- Matter can neither be created nor destroyed.
2. Law of Definite Proportions
- A given compound always contains exactly the same proportion of elements by weight.
- The validity of this law has been confirmed by various experiments.
- It is sometimes also referred to as Law of Definite Composition.
3. Law of Multiple Proportions
- If two elements can combine to form more than one compound, the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other element are in the ratio of small whole numbers.
4. Gay Lussac’s Law of Gaseous Volumes
- When gases combine or are produced in a chemical reaction, they do so in a simple ratio by volume, provided all gases are at the same temperature and pressure.
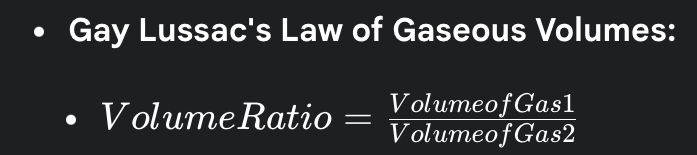
5. Avogadro’s Law
- Equal volumes of all gases at the same temperature and pressure should contain an equal number of molecules.

6. Dalton’s Atomic Theory
- Matter consists of indivisible atoms.
- All atoms of a given element have identical properties, including identical mass. Atoms of different elements differ in mass.
- Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine in a fixed ratio.
- Chemical reactions involve the reorganization of atoms. These are neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
7.Atomic and Molecular Masses
- Atomic Mass: The mass of an atom of a chemical element expressed in atomic mass units (amu).
- Molecular Mass: The sum of the atomic masses of all atoms in a molecule of the substance.

PYQ From the topic


