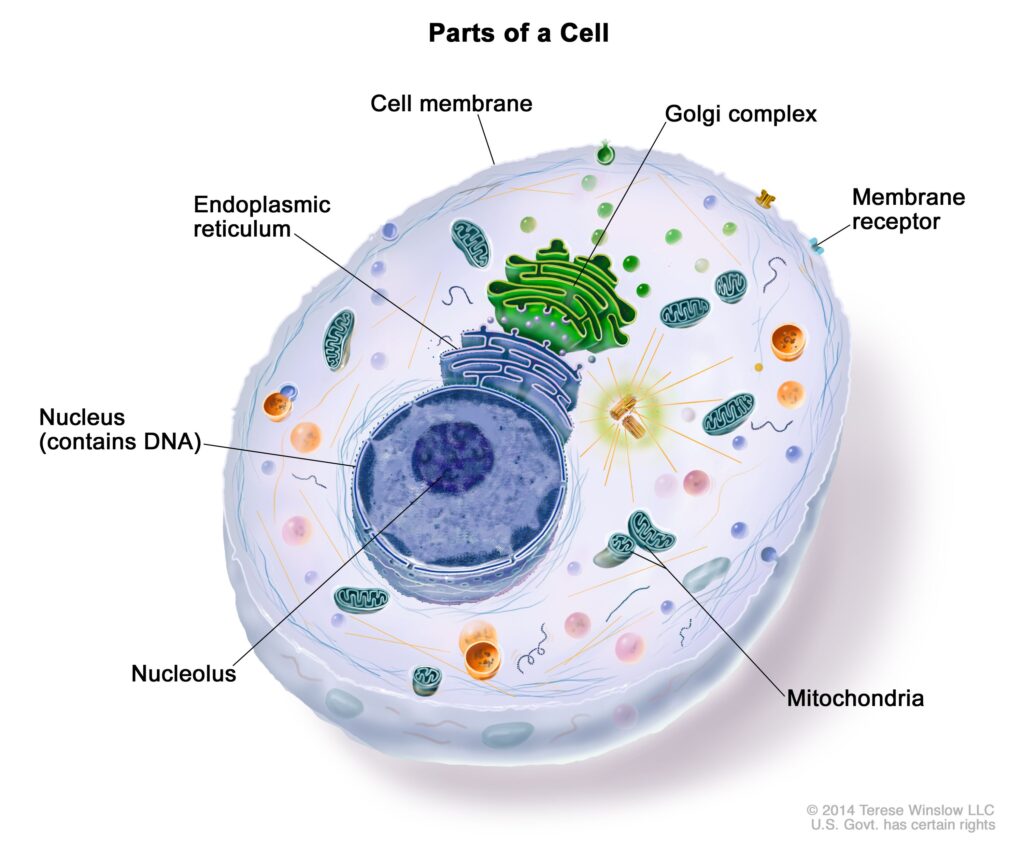
Introduction: The cell, often referred to as the basic unit of life, is an intricate and dynamic entity that serves as the foundation of all living organisms. The exploration of cells has been a cornerstone in the field of biology, unraveling the mysteries of life at its most fundamental level. This essay delves into the remarkable world of cells, examining their structure, functions, and the profound impact they have on the continuum of life.
Cell Structure: At its core, a cell is a complex and organized structure, embodying a diverse array of components that work in harmony to sustain life. The two primary categories of cells, prokaryotic and eukaryotic, showcase the evolution of cellular complexity. Prokaryotic cells, found in bacteria and archaea, lack a defined nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells, present in plants, animals, fungi, and protists, boast a nucleus and specialized organelles within their membrane-enclosed boundaries.
Within the eukaryotic cell, the nucleus stands as a repository of genetic information, housing the DNA molecules that dictate the organism’s characteristics. Surrounding the nucleus, the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and mitochondria form a network of interconnected structures, each playing a crucial role in the synthesis, modification, and distribution of proteins and energy production.
Functions of the Cell: The functions of a cell are myriad, reflecting its status as the fundamental unit of life. Cellular metabolism, the sum of chemical reactions within a cell, involves processes such as glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation, all of which contribute to energy production. The cell membrane, a selectively permeable barrier, regulates the passage of substances, ensuring a stable internal environment.
Additionally, cells engage in reproduction, a vital process for the perpetuation of life. While prokaryotic cells replicate through binary fission, eukaryotic cells undergo mitosis or meiosis, producing genetically identical or diverse offspring, respectively. The intricacies of cell cycle regulation and checkpoints underscore the precision required for successful reproduction.
Cellular Communication: Communication between cells is a pivotal aspect of multicellular organisms, orchestrating the coordination of diverse cellular activities. Signaling pathways, mediated by molecules such as hormones and neurotransmitters, enable cells to convey information, responding to external stimuli and maintaining homeostasis. The concept of signal transduction, involving receptor proteins and intracellular cascades, illustrates the nuanced language cells use to communicate with one another.
The Impact of Cell Research: Cell biology research has far-reaching implications across various scientific disciplines and practical applications. Medical advancements, such as vaccines, antibiotics, and gene therapies, owe their success to a deep understanding of cellular mechanisms. Furthermore, insights gained from studying cells have fueled breakthroughs in fields like genetics, developmental biology, and regenerative medicine, offering promising avenues for addressing complex health challenges.
Summary: In essence, the cell represents the symphony of life, where diverse components harmonize to create and sustain living organisms. The ongoing exploration of cells continues to unravel the intricacies of life itself, offering a profound appreciation for the elegance and complexity inherent in the smallest units of existence. As technology – advances and interdisciplinary collaboration thrives, the journey into the cellular realm promises to unlock new dimensions of knowledge and pave the way for innovative solutions to pressing global challenges.
References:
- Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, et al. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 6th edition. New York: Garland Science; 2014.
- Lodish H, Berk A, Zipursky SL, et al. Molecular Cell Biology. 4th edition. New York: W. H. Freeman; 2000.
- Cooper GM. The Cell: A Molecular Approach. 2nd edition. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates; 2000.
- Lodish H, Berk A, Kaiser CA, et al. Molecular Cell Biology. 7th edition. New York: W. H. Freeman; 2012.
- Campbell NA, Reece JB, Urry LA, et al. Biology. 9th edition. San Francisco: Pearson; 2011.